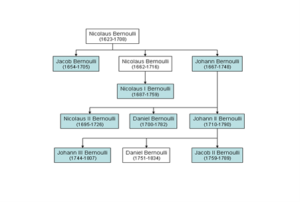
The Bernoulli family was one of the most prominent families in the history of mathematics, producing a remarkable line of mathematicians who made significant contributions to several areas of mathematics and science, particularly in calculus, probability theory, hydrodynamics, and mathematical physics. Their achievements span several generations, and their influence on the development of modern mathematics remains profound.
Here’s an overview of the mathematician Bernoulli family, focusing on the key figures and their contributions:
The Bernoulli Mathematicians and Their Contributions
1. Jacob Bernoulli (6 January 1654– 16 August 1705)
Jacob was a pioneer in the development of probability theory, mathematical analysis, and calculus. He is best known for formulating Bernoulli’s Law of Large Numbers, which states that as the number of trials in a random experiment increases, the average of the results will converge toward the expected value. His book Ars Conjectandi (1713, posthumously) helped lay the foundations of modern probability theory and introduced the Bernoulli distribution.
Jacob’s work on infinite series and probability influenced many later mathematicians, including Pierre-Simon Laplace and Abraham de Moivre.
2. Johann Bernoulli (6 August 1667– 1 January 1748)
Johann was a leading figure in the development of calculus, differential equations, and fluid mechanics. He is known for solving the brachistochrone problem (the curve of fastest descent), which is one of the foundational problems in calculus of variations. He worked closely with Leonhard Euler and played a key role in promoting Leibniz’s calculus in Europe. Johann also contributed to hydrodynamics through his work on Bernoulli’s principle, which explains the relationship between fluid velocity and pressure.
Johann mentored many great mathematicians, including Euler, and his work shaped much of fluid dynamics and calculus.
3. Nicolaus I Bernoulli (21 October 1687- 29 November 1759)
Nicolaus (I) Bernoulli was a nephew of Jacob Bernoulli and Johann Bernoulli. His early education involved studying mathematics with his uncles. In fact it was Jacob Bernoulli who supervised Nicolaus’s Master’s degree at the University of Basel which he was awarded in 1704. Five years later he was received a doctorate for a dissertation which studied the application of probability theory to certain legal questions.
4. Nicolaus II Bernoulli (6 February 1695 – 9 August 1726)
Nicolaus II was was one of the many talented members of the Bernoulli family which included his father, Johann Bernoulli, and his brother, Daniel Bernoulli. While his father and brother are perhaps more widely known for their contributions to mathematics, Nicolaus II made significant contributions in his own right, especially in the fields of calculus and the theory of probability.
He is also noted for his work in mathematical analysis and the application of mathematics to mechanics. Unfortunately, Nicolaus’s career was cut short when he died young at the age of 31, but his legacy is still part of the broader Bernoulli family’s influence on the development of mathematics.
5. Daniel Bernoulli (8 February 1700– 27 March 1782)
Daniel, one of Johann Bernoulli’s sons is perhaps the most famous of the Bernoulli family, known for his contributions to fluid mechanics and probability theory. His Bernoulli’s principle in fluid dynamics is one of the most important discoveries in physics, explaining how changes in the speed of a fluid relate to changes in pressure. His book Hydrodynamica (1738) laid the groundwork for the study of fluid dynamics and kinetic theory. Daniel also worked on probability theory and contributed to the stochastic processes field.
Daniel’s work was crucial in the development of mathematical physics, and his discoveries continue to impact fields such as aerodynamics, engineering, and thermodynamics.
7. Johann II Bernoulli (18 May 1710– 17 July 1790)
Johann II, another of Johann Bernoulli’s sons, was a mathematician who contributed to mathematical analysis but didn’t achieve the same level of recognition as his father or brother Daniel. He was a professor at the University of Basel and worked on analysis and calculus.
Johann II was also involved in the teaching of many prominent mathematicians, continuing the Bernoulli tradition of academic influence.
8. Jean (Johann III) Bernoulli (4 November 1744– 13 July 1807)
Jean was another of Johann’s grandsons. His work focused on mechanics and mathematical physics, contributing to the study of elasticity and fluids.
Jean was also involved in the scientific community of the time, but like Nicolaus II, his contributions were more focused on continuing the family’s legacy rather than breaking new ground.
Legacy of the Bernoulli Family
The Bernoulli family produced a long line of mathematicians whose discoveries helped shape the development of modern mathematics, calculus, fluid mechanics, probability theory, and mathematical physics. Their work continues to influence various fields, including:
• Probability and Statistics: The Bernoulli distribution and the Law of Large Numbers remain foundational concepts.
• Fluid Mechanics: Bernoulli’s principle is fundamental in the study of aerodynamics and hydrodynamics.
• Mathematical Analysis: The family’s work on infinite series, differential equations, and calculus of variations has had a lasting impact.
The Bernoulli family was a dynasty of mathematicians whose work spanned many generations. Johann Bernoulli, along with his brothers and sons, laid the groundwork for important developments in calculus, probability theory, and fluid mechanics. Their legacy is still alive today in the mathematical and scientific fields, and the name “Bernoulli” is synonymous with some of the most important concepts in modern mathematics. Their achievements continue to inspire mathematicians, physicists, and engineers.
Bernoulli Family Tree